When GPT 3.5 was released in November 2022, I, like many others, thought: “Qualitative analysis has been solved.” The ChatGPT interface was user-friendly, regardless of technical expertise, and its text generation and summarization capabilities seemed sufficient for most use cases. The launch of GPT 4 in March 2023 only strengthened the belief that LLMs, in geek-speak, were Turing-complete for qualitative research analysis.
However, when I actually put GPT and other state-of-the-art LLMs like Claude and Gemini to the test for real qualitative analysis, the results were far from ideal. The summaries they generated were often incomplete, missing key themes or nuances from the data. Worse, the models frequently hallucinated, inserting details that were not present in the source material. The reports they produced were short and schematic, lacking the depth and richness required for serious qualitative research. It quickly became clear that this was not just an issue of prompt engineering—it was a fundamental limitation of the models themselves.
I developed QualBot to address these issues. While LLMs could summarize and generate text reasonably well, they struggled with the rigor and context sensitivity that qualitative analysis demands. QualBot was built specifically for qualitative thematic analysis, focusing on three key areas: providing complete and accurate thematic summaries, maintaining context without hallucinating information, and generating detailed, well-structured reports. By integrating targeted models, custom heuristics, and iterative analysis, QualBot can deliver deeper insights and ensure that the nuances of participant responses are preserved, producing reports that are both thorough and reliable.
LLMs continue to evolve rapidly, and with the release of models like GPT-4o or Claude Sonnet, we’ve seen significant improvements in performance. These models have become faster, more cost-effective, and better at handling complex tasks, including qualitative analysis. Their ability to produce more coherent and accurate summaries has reduced the number of iterations QualBot needs to go through to refine its outputs. As these advancements continue, QualBot leverages these models where appropriate, while still providing the structure and depth that general-purpose LLMs alone can’t fully achieve. This synergy means faster turnaround times and more efficient analysis without sacrificing quality.
Beyond these efficiency gains, emerging AI technologies are unlocking exciting new opportunities for qualitative researchers. As AI becomes more embedded in qualitative research workflows, it’s paving the way for not just enhanced analysis but also entirely new methods of exploring complex human behaviors and experiences. Below, we present several ideas that could serve as a roadmap of sorts for future QualBot features.
Qualitative Co-pilot
The most obvious next step is a co-pilot mode where AI supports researchers by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as coding, data sorting, and preliminary theme identification, freeing up researchers to concentrate on gaining deeper insights and drawing meaningful conclusions. Researchers maintain full control, reviewing and refining the AI’s output at each stage of the analysis process.
For example, agentic RAG systems such as LlamaIndex workflows use multi-agent architectures, where individual agents are responsible for managing subsets of documents, performing searches, and summarizing results, while a top-level agent orchestrates these sub-agents, retrieves tools, and executes a Chain-of-Thought process to provide highly relevant answers based on document relevance and re-ranking.
Co-pilot mode is not about replacing human expertise but enhancing it to create super-human results. By allowing AI to take on the repetitive, low-level tasks, researchers can dedicate more of their time to high-level thinking and interpretation. This augments human intuition and domain knowledge, leading to more efficient and accurate outcomes while maintaining the depth and rigor that qualitative research demands.
AI Augmentation
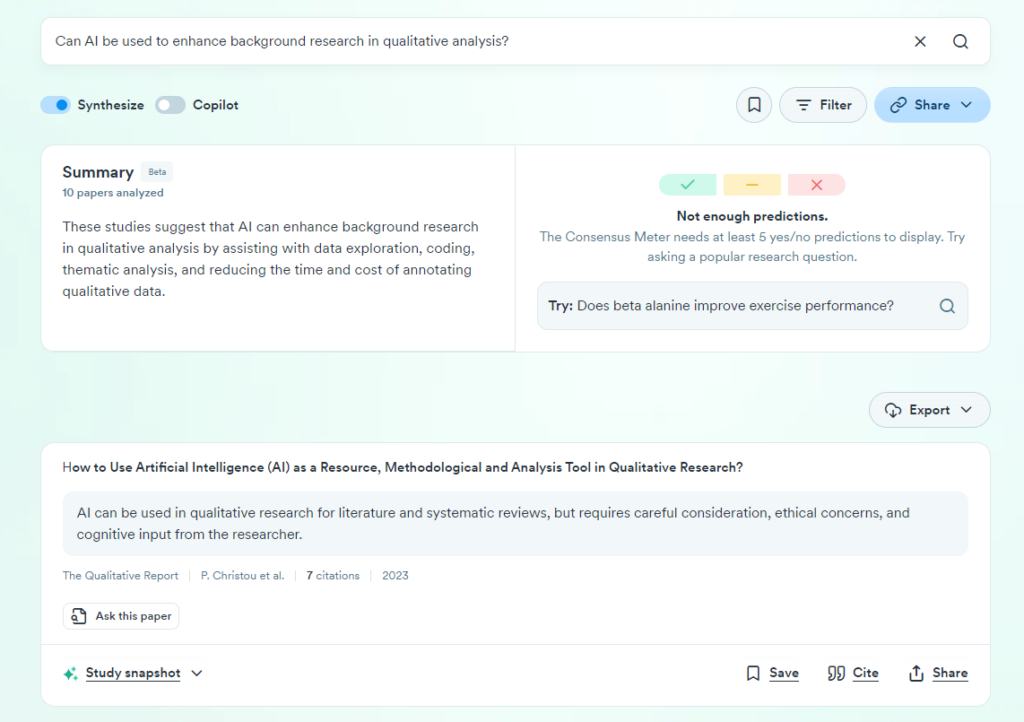
AI is increasingly capable of automating background research for qualitative studies. By leveraging emerging technologies, researchers can use AI to efficiently gather and synthesize information from a vast array of online sources, including scientific literature, news articles, and specialized databases.
In 2024, AI-driven automated online search tools have advanced significantly. These tools allow for real-time data retrieval from the web, ensuring that researchers have access to the most up-to-date information. For instance, tools like Consensus offer specialized capabilities for synthesizing scientific research, helping users quickly understand the consensus within academic literature on a given topic. This can be invaluable for generating literature reviews or understanding the state of knowledge in a particular research field.
AI technologies can autonomously crawl through the latest publications, summarize findings, and present researchers with key insights—saving hours of manual work. As these tools evolve, they will integrate deeper search capabilities, allowing for not just web searches but also the retrieval of proprietary or niche data sources relevant to qualitative research topics.
By incorporating these AI technologies into qualitative research workflows, researchers can enhance their understanding of the subject at hand, ensuring that their studies are grounded in the latest information and providing a stronger foundation for more nuanced analysis.
Specialized Analytics
The current AI toolkit can be expanded to cover a broad range of qualitative research methods, such as grounded theory, ethnography, and mental mapping.
- Grounded Theory: AI can assist in grounded theory by identifying recurring patterns and codes in data, helping researchers move from raw transcripts to conceptual frameworks. AI tools can accelerate the coding process and suggest relationships between concepts, allowing researchers to build theories systematically.
- Ethnography: For ethnographic research, AI can support the analysis of large datasets, such as participant observations, interviews, and even multimedia data like video recordings. AI can identify cultural patterns, behaviors, and social interactions, providing researchers with key insights that would otherwise take much longer to analyze manually.
- Cognitive Testing: Cognitive interviewing is used to explore how participants comprehend, recall, or interpret specific material. AI can assist by analyzing patterns in participant feedback, identifying common points of confusion or misinterpretation, and flagging discrepancies across responses. This allows researchers to refine survey instruments or communication strategies more effectively.
- Mental Mapping: AI tools can also assist in mental mapping, where participants’ cognitive models or perceptions of specific topics are visualized. By processing responses and grouping related ideas, AI can generate these maps more efficiently, highlighting key connections and themes that may not be immediately obvious and generating computational fuzzy logic models that can be used simulate hypothetical outcomes.
Multimedia Reports
Generative AI has made significant strides in video avatar technology, opening up exciting possibilities for automated video reports in qualitative research. Tools like NVIDIA’s Avatar Cloud Engine (ACE), Synthesia or Veed are making it possible to create highly realistic, AI-driven avatars that can present research findings with natural facial expressions and synchronized speech.
Automated video reports would enable researchers to generate dynamic presentations where avatars narrate key themes, display participant quotes, and even present visuals like thematic maps. This approach can make complex qualitative data more accessible and engaging for stakeholders, transforming how insights are communicated.
Ethical AI and Research Transparency
As AI becomes more integral to research, ethical considerations are increasingly critical. Researchers must ensure transparency in how AI processes data and makes decisions. This involves clear communication about the algorithms used, their data sources, and how they reach conclusions. Additionally, safeguarding the privacy of respondents is essential. Ensuring that AI models comply with GDPR and other data protection regulations will be a central part of maintaining trust and integrity in the research process.
AI holds the potential to reduce researcher bias in qualitative research by providing more objective and balanced insights. While human researchers may unconsciously influence data interpretation, AI can offer a data-driven approach, ensuring that findings are based on patterns in the data rather than subjective interpretation. For instance, tools like QualBot can analyze large datasets impartially, helping to highlight trends that might otherwise be overlooked or interpreted with bias.
Finally, AI can enhance data integrity by maintaining an audit trail of how data is processed and analyzed. This transparency helps ensure that researchers can trace back the steps taken during the analysis, offering verifiable proof of how conclusions were drawn. AI can log every transformation, from initial data cleaning to thematic coding, ensuring full accountability. This is particularly useful for meeting ethical standards in research where transparency and data verifiability are key.
These are just a few of the future updates we expect to develop for QualBot. From AI-powered co-pilot modes that streamline the workflow to automated video reports with lifelike avatars, QualBot will continue to integrate the latest in generative AI, enhancing both the depth and efficiency of qualitative research.
As AI continues to evolve, these advancements open up new possibilities—such as improved background research automation, expanded multimodal analysis capabilities, and enhanced tools for ethical, bias-free research. Whether it’s identifying hidden patterns in data or generating dynamic, multimedia reports, the future of qualitative research is becoming more innovative and interactive than ever.
If you want to be part of this exciting journey and be the first to try these updates, sign up for the QualBot app today and experience the future of qualitative research firsthand!
Sign up https://app.qualbot.io/